

Cardiologists can make a diagnosis of heart failure via physical examination, results from an electrocardiogram (ECG, a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart), a chest X-ray to see whether the heart is enlarged, and other tests. As a result, an insufficient number of calcium ions are available to trigger a sufficient contractile force.Ĭardiologists ( cardi = “heart” ologist = “one who studies”) are doctors who specialize in treating heart diseases, including heart failure. Heart failure occurs when the endoplasmic reticula of cardiac muscle cells do not function properly. The wall of the heart is composed of cardiac muscle tissue. Left untreated, heart failure can lead to kidney failure and failure of other organs. Rather, it means that the heart can’t pump with sufficient force to transport oxygenated blood to all the vital organs. Heart failure does not mean that the heart has stopped working. Heart failure is just one of many disabling heart conditions. This is primarily due to our sedentary lifestyle and our high trans-fat diets. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. In muscle cells, a specialized SER called the sarcoplasmic reticulum is responsible for storage of the calcium ions that are needed to trigger the coordinated contractions of the muscle cells. Functions of the SER include synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones detoxification of medications and poisons and storage of calcium ions. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is continuous with the RER but has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface. This is the case with cells of the liver, for example. Since the RER is engaged in modifying proteins (such as enzymes, for example) that will be secreted from the cell, you would be correct in assuming that the RER is abundant in cells that secrete proteins. If the phospholipids or modified proteins are not destined to stay in the RER, they will reach their destinations via transport vesicles that bud from the RER’s membrane (Figure 1).

These modified proteins will be incorporated into cellular membranes-the membrane of the ER or those of other organelles-or secreted from the cell (such as protein hormones or enzymes). The RER also makes phospholipids for cellular membranes. Ribosomes transfer their newly synthesized proteins into the lumen of the RER where they undergo structural modifications, such as folding or the acquisition of side chains. (credit: modification of work by Louisa Howard) This transmission electron micrograph shows the rough endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles in a pancreatic cell. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is so named because the ribosomes attached to its cytoplasmic surface give it a studded appearance when viewed through an electron microscope (Figure 2).įigure 2. The membrane of the ER, which is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins, is continuous with the nuclear envelope. The hollow portion of the ER tubules is called the lumen or cisternal space. However, these two functions are performed in separate areas of the ER: the rough ER and the smooth ER, respectively.
#WHAT DOES THE ROUGH ER DO SERIES#
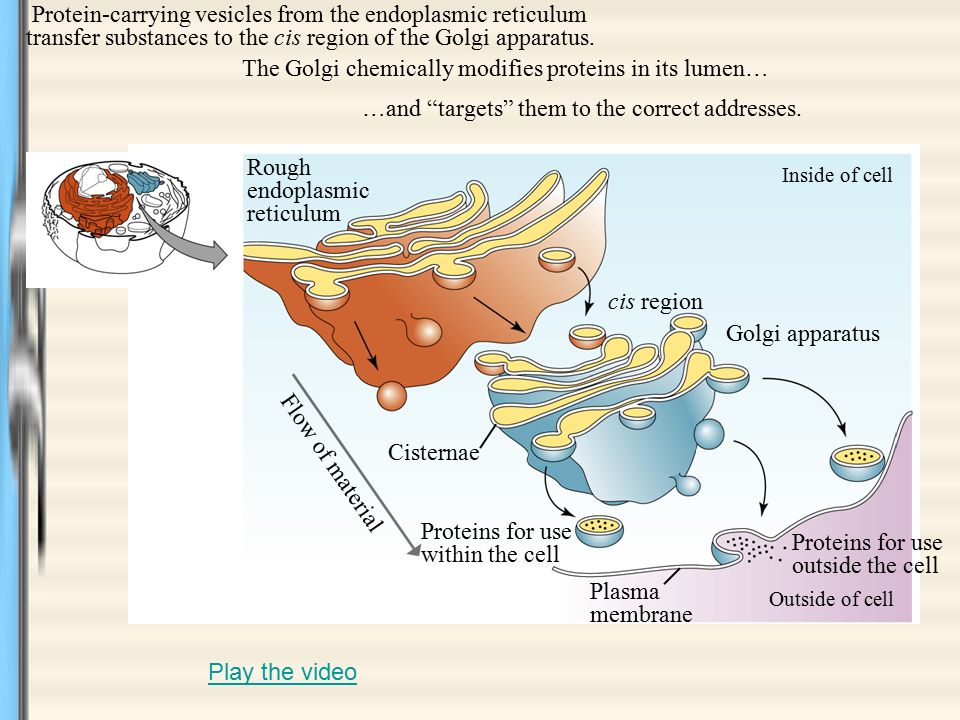
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (Figure 1) is a series of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that collectively modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids. After its synthesis is complete, it exits as integral membrane protein of the vesicle that bud from the Golgi’s trans face and when the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane the protein becomes integral portion of that cell membrane. As the protein passes along the Golgi’s cisternae, it is further modified by the addition of more carbohydrates. Vesicles with the integral protein bud from the ER and fuse with the cis face of the Golgi apparatus. The endomembrane system does not include the membranes of either mitochondria or chloroplasts.įigure 1 illustrates the connections of the endomembrane system as a (green) integral membrane protein in the ER is modified by attachment of a (purple) carbohydrate. Although not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the endomembrane system because, as you will see, it interacts with the other endomembranous organelles. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. The endomembrane system ( endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles (Figure 1) in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. (credit: modification of work by Magnus Manske) The RER’s membrane also sometimes modifies proteins. Membrane and secretory proteins are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
